1. 引言 Intro
扩展 dense 模型难度越来越大。稀疏模型(Sparse Model)可以在不显著增加训练成本的情况下扩展模型规模。推理阶段仅激活部分参数,因此相比同等参数量的稠密模型,推理速度更快
2. Transformer 中的 MoE 结构
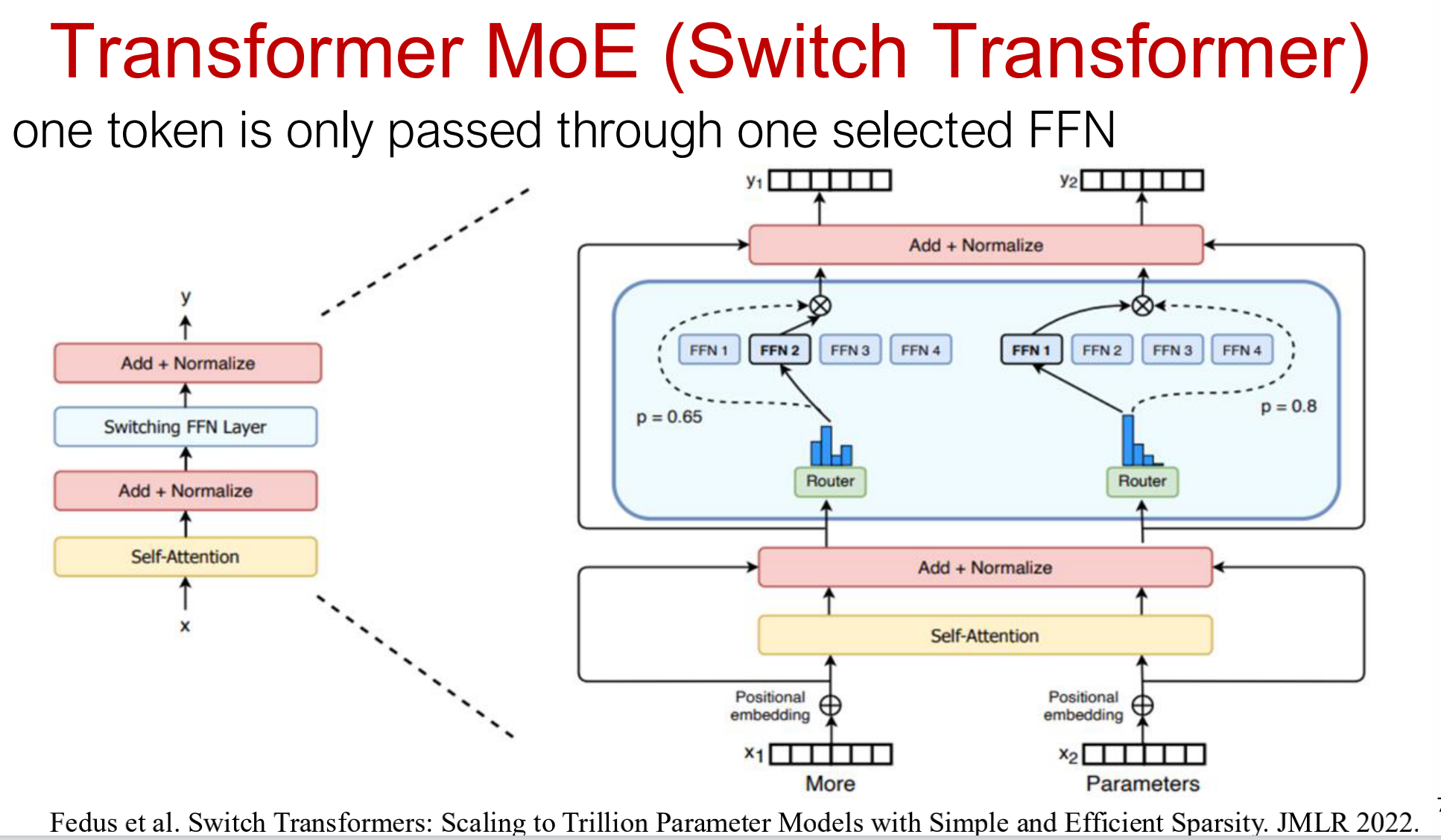
2.1 MoE 模块替换 FFN
Transformer 中的 前馈网络(FFN) 替换为以下结构:
- 多个小专家(Experts):每个专家是一个独立的 FFN;
- 门控网络(Gating Network):根据输入 token 决定激活哪些专家
2.2 门控与专家计算公式
2.2.1 门控函数
\(G_\sigma(x) = \text{Softmax}(x \cdot W_g)\)
其中:
- $x$:输入 token 表示;
- $W_g$:门控网络参数;
- Softmax 输出每个专家的概率权重。
2.2.2 专家加权输出
\(y = \sum_{i=1}^{n} G(x)_i E_i(x)\)
其中:
- $E_i(x)$:第 $i$ 个专家输出;
- $G(x)_i$:对应专家的激活概率
2.2.3 Top-k 门控机制
\[G(x) = \text{Softmax}(\text{KeepTopK}(H(x), k))\]仅选择概率最高的 $k$ 个专家执行计算
2.3 共享与路由专家 (Shared & Routed Experts)
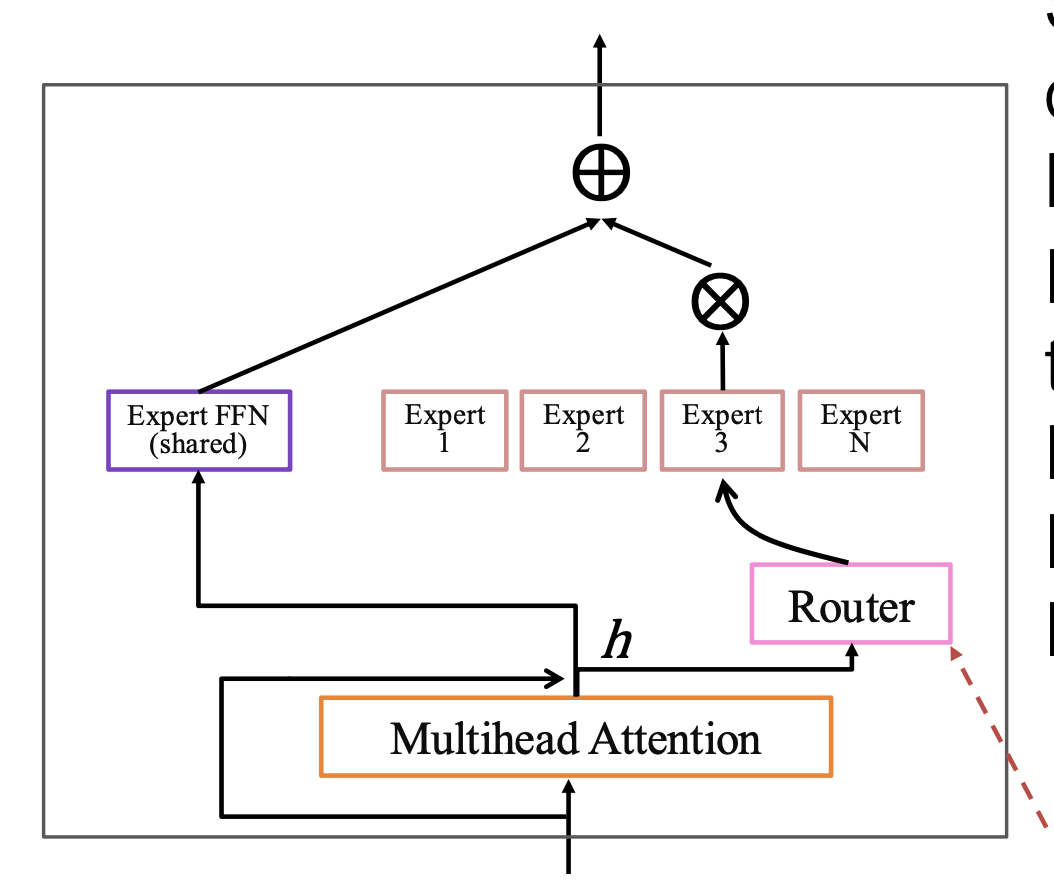
2.3.1 共享专家(Shared Expert):
负责计算模型中的通用知识(common knowledge), 即所有 token 都会经过这些专家,以保证全局一致性与稳定性。
2.3.2 路由专家(Routed Experts):
负责计算与 特定 token 相关的知识(token-specific knowledge), 每个 token 通过 门控机制(routing network) 被动态分配到不同的专家中
每一层选择被激活的专家是不同的
2.4 MoE 的过拟合问题
每个样本只激活部分专家;
当数据量太少时,不同专家看到的数据分布太小
导致专家学习到的特征不具备普适性
2.5 专家学习行为与几何理解
2.5.1 专家学习行为
-
编码器(Encoder)中的专家 往往会在训练中专注于某些 token 群体或浅层概念, 例如标点符号、专有名词等局部特征
-
解码器(Decoder)中的专家 通常表现出更弱的特化(specialization), 即不同专家之间的分工不明显
-
在多语言模型(multilingual setup)中, 专家不会专门对应某一种语言,
- 这是因为 token 路由机制 与 负载均衡策略(load balancing) 会强制使不同语言的 token 混合分配到多个专家中,
- 从而防止语言层面的过度聚集
2.5.2 几何解释
专家路由的几何解释(Geometric Interpretation of Expert Routing)
当使用 KeepTop1(即每个 token 只选择一个专家)并且共有 3 个路由专家 时, 路由过程可以从几何角度理解为:
在专家的特征空间中,模型通过学习线性边界(linear boundaries), 将输入向量划分到距离最近的专家中心点(expert centroid)所对应的区域中。
也就是说,门控网络(gating network)在隐空间中学习出一个类似于线性分类面的结构, 每个区域代表一个专家的“职责范围”
3. MoE 的训练与推理机制
3.1 EP(Expert Parallelism)并行
3.1.1 基本原理
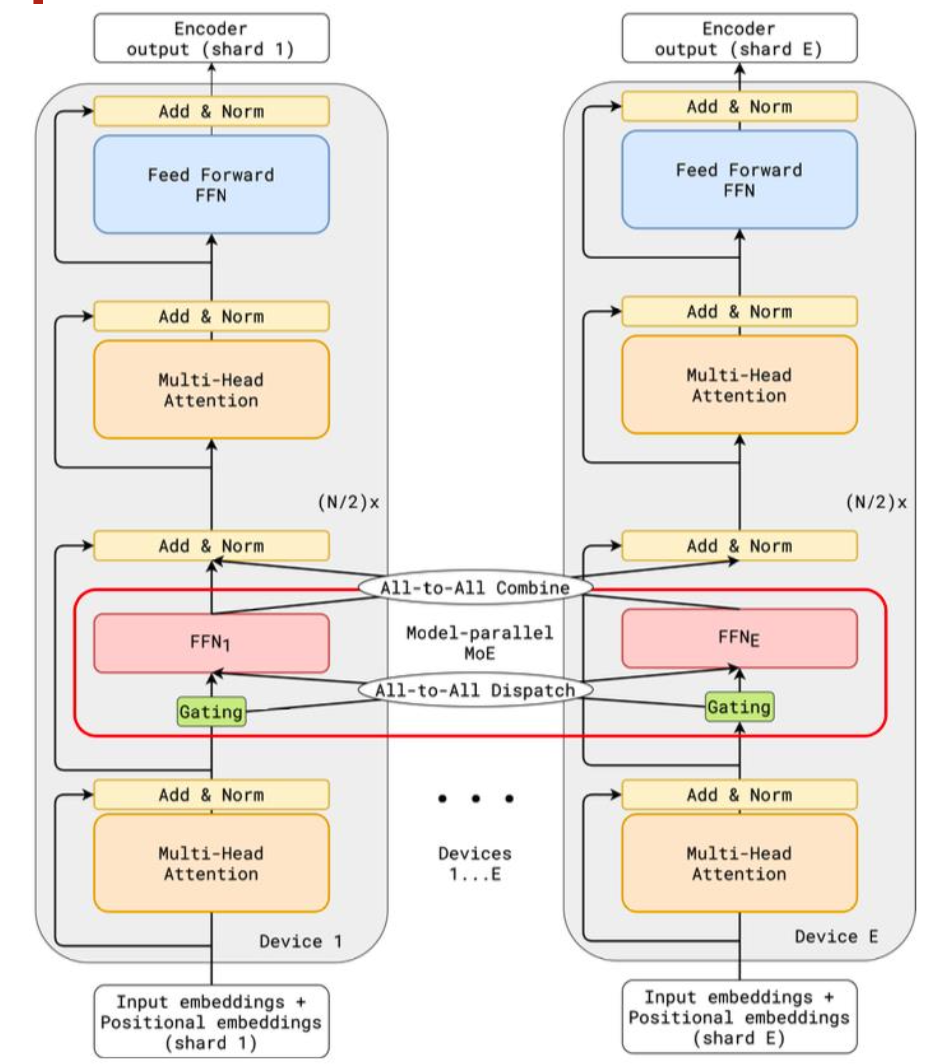
- 每个 专家(Expert) 仅放置在一个工作设备(worker device) 上;
- 其他网络组件(例如注意力层、嵌入层等)会在所有设备上进行完整复制;
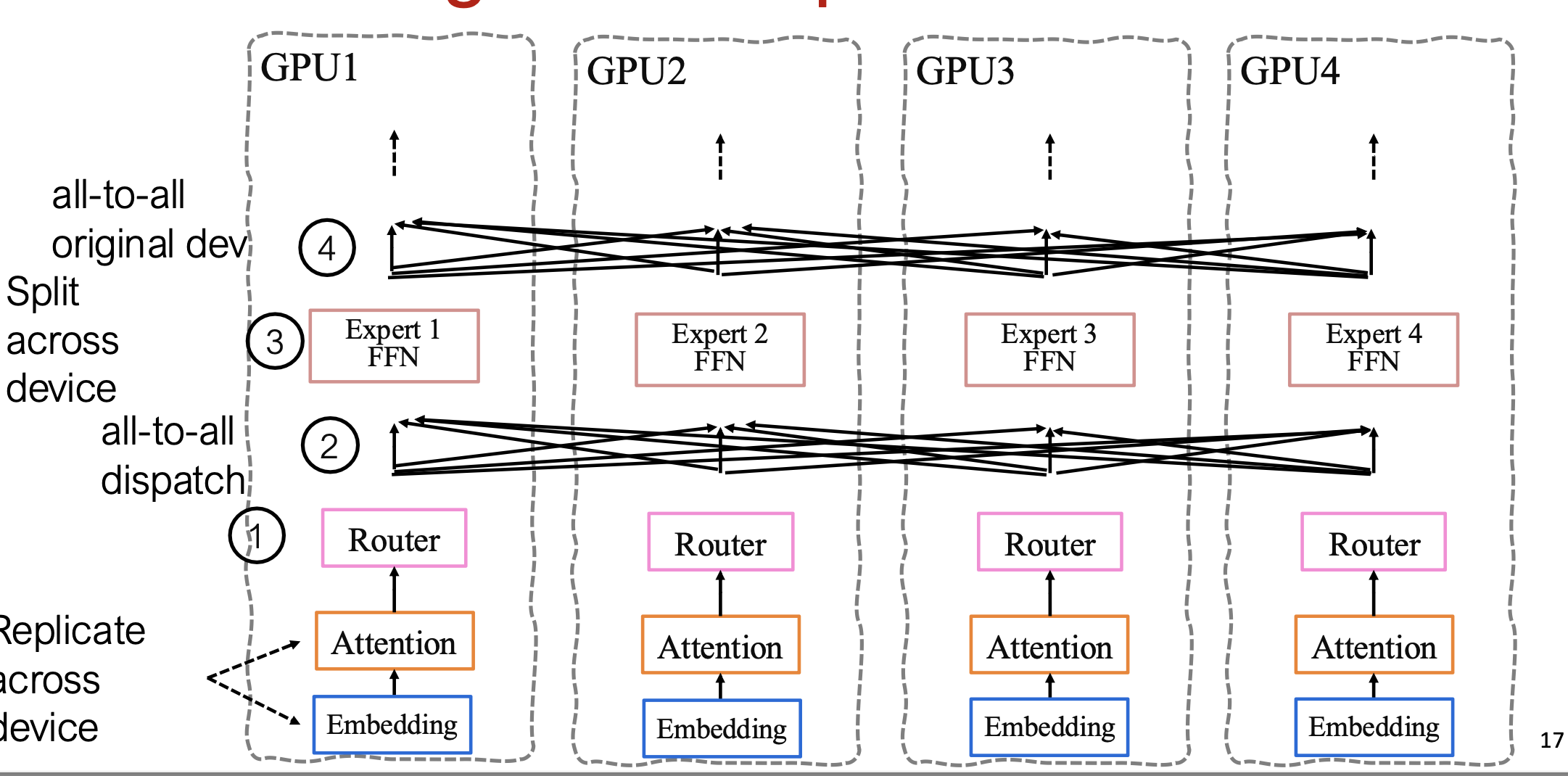
- 因此,模型训练过程中需要依赖all-to-all communication 来在不同设备间交换 token 数据
参考:Lepikhin et al. GShard: Scaling Giant Models with Conditional Computation and Automatic Sharding. ICLR 2021
3.1.2 交错专家设计(Interleaving Experts)
GShard 的交错专家设计(Interleaving Expert) 指的是:
- 并非所有 Transformer 层都使用专家结构,而是每隔一层启用 MoE 层
- 以在性能、训练稳定性与通信成本之间取得平衡
3.2 负载均衡损失 (Load Balance Loss)
3.2.1 问题背景
在 MoE 模型中,Router(路由器) 会根据输入 token 的特征决定该 token 该被送到哪个专家 (Expert)
但如果不加约束,模型可能学会只使用少数几个专家—— 造成:
- 某些专家被过度使用;
- 其他专家几乎闲置;
- 模型整体容量浪费,训练不稳定。
为此,需要一个负载均衡损失(Load Balance Loss) 来约束专家的使用分布。
3.2.2 Expert-Level Balance Loss
$$
L_{\text{ExpBal}} = \alpha_1 M \sum_{i=1}^{M} f_i P_i
\[其中: * $M$:专家数; * $\alpha_1$:权重; * $f_i$:专家i实际接收比例; * $P_i$:专家平均路由概率。 通过最小化这个损失,模型会倾向让 ( f_i ) 与 ( P_i ) 在所有专家上分布更均匀。 #### 3.2.3 自定义式\]f_i = \frac{\text{tokens to expert } i}{\text{tokens total}}
$$
\[P_i = \frac{1}{\text{tokens}} \sum_{t=1}^{\text{tokens}} s_{i,t}\]- $f_i$:实际使用率;
- $P_i$:Router 分配意图;
- $L_{\text{ExpBal}}$:惩罚两者不一致。
3.2.4 直观理解
- $f_i$ → 代表专家的实际使用率
- $P_i$ → 代表 Router 的分配意图(期望使用率)
- $L_{\text{ExpBal}}$ → 惩罚两者不一致的情况(即部分专家被过度或不足使用)
通过这个损失项:
- Router 被引导让每个专家接收到接近均等数量的 token;
- 避免「所有 token 都被路由到一个专家」的情况;
- 提升训练稳定性与计算资源利用率
3.3 推理阶段优化
3.3.1 性能瓶颈
显存需求高,因所有专家常驻 GPU
3.3.2 系统优化策略
系统设计目标:
- 最小化每个设备的关键数据路径(critical data path), 并最大化整体可用的内存带宽(aggregate memory bandwidth)。
具体策略:
-
分组与路由优化: 将具有相同关键数据路径的 token 进行分组与路由, 以减少每个设备上的数据访问量,并实现最大化的整体带宽利用。
-
通信调度优化: 通过并行协调(parallelism coordination)来优化通信调度, 提高跨设备数据传输的效率。
-
算子优化: 针对 Transformer 层与 MoE 模块的核心计算核(kernel)进行优化, 以提升单设备的计算性能。
3.4 并行方式结合
3.4.1 EP 并行与 TP 并行
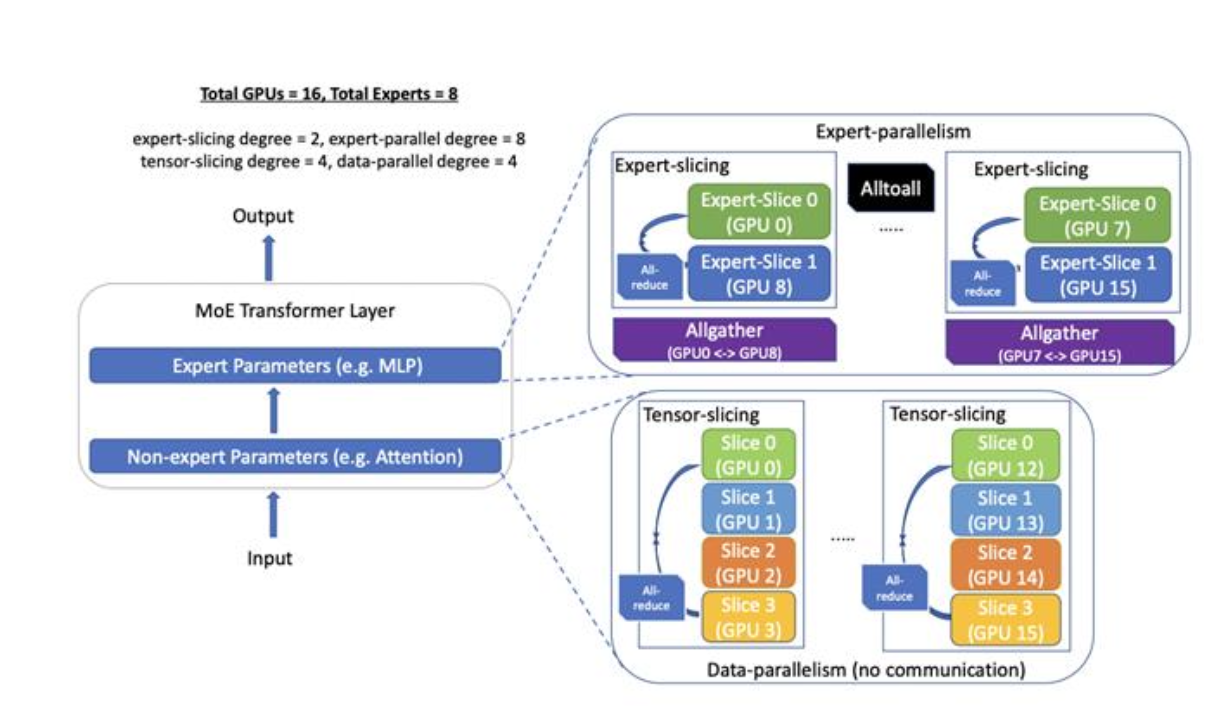
专家并行(Expert Parallelism) / 专家切分(Expert Slicing):
- 将所有被分配到同一专家的输入 token 归为一组,使它们共享相同的关键数据路径(critical data path)。
- 然后使用专家并行,在不同设备之间并行处理具有不同关键路径的 token 组, 以提升整体吞吐和设备利用率。
张量并行(Tensor Parallelism) / 张量切分(Tensor Slicing):
- 将非专家部分的参数(例如注意力层中的权重)在多台设备间划分(通常在同一节点内完成)。
- 在此基础上,还可以进一步结合数据并行(Data Parallelism),
- 以同时利用样本级并行与参数级并行,从而实现多维度的分布式训练加速。
参考:Rajbhandari et al (2022). DeepSpeed-MoE: Advancing Mixture-of-Experts Inference and Training to Power Next-Generation AI Scale.
3.5 算子优化 (Kernel Optimization)
MoE 特定优化(MoE Specific Optimizations):
-
将 门控函数(gating function) 融合为单一计算核(single kernel),减少多次函数调用带来的开销
-
使用稠密的 token-到-expert 映射表(dense token-to-expert mapping table),提升数据访问与路由效率
举个例子(Top-1 路由):
稀疏方式:
{token_0: expert_2, token_3: expert_5, token_5: expert_2, ...}
→ 查找专家时,需要遍历或聚合哈希结构。
稠密方式:
expert_id = [2, 5, 2, 0, 4, 1, ...] # 与 token index 一一对应
→ 可以直接用索引张量做 gather/scatter 操作,一步完成。
优化结果: MoE 相关计算核(kernel)延迟降低了 超过 6 倍(over 6× reduction in latency)。
4. DeepSeek MoE 实践
4.1 模型结构
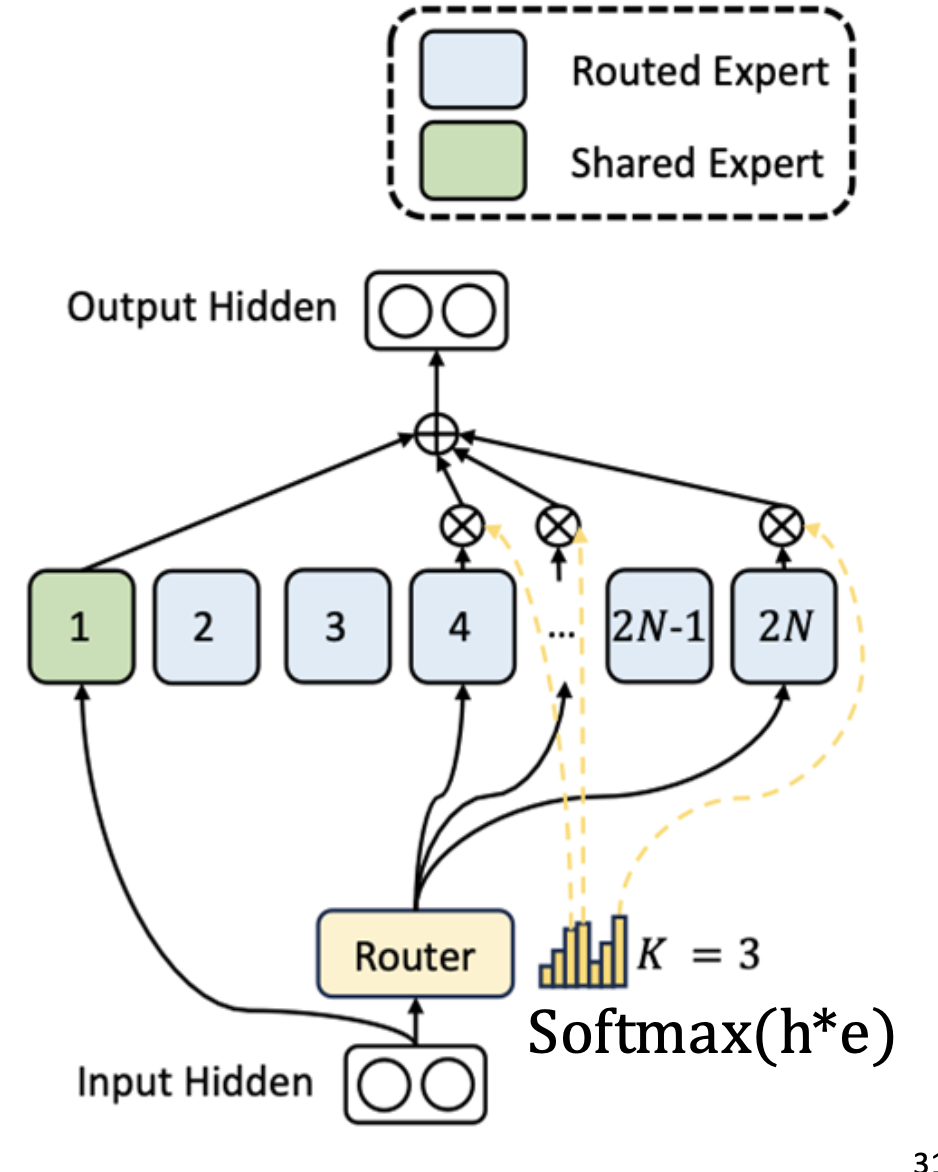
-
更细粒度的专家:原本的一个 FFN 被拆分为 k 更小的子专家(sub-experts)。原本有 N 个专家,则总专家数变为 k * N。
-
Shared Experts + Routed Experts(共享专家 + 路由专家)
-
Shared Experts(绿色):对所有 token 通用,学习全局知识(如语言常识、句法结构等);
-
Routed Experts(蓝色):由 Router 动态选择,只处理部分 token,学习特定语义或模式。
- 加权路由激活,多个专家加权激活
4.2 模型配置 (V3-670B)
Vocab: 129,280
dimension=7168
num layer=61
num dense layer=3 (lowest)
num head = 128
dim ffn (inter dim)=18432
moe dim = 2048
num shared experts = 1
num routed experts = 256
num activated experts = 8
num expert group=8
num limited group=4
Top-8 个激活专家
注意力头数 = 128
专家数量 = 256 + 1
FFN采用。SwiGLU激活函数
4.3 负载均衡改进
4.3.1 Expert-Level Balance Loss
避免专家塌陷(routing collapse)
来自标准的 DeepSpeed-MoE 思路,但 DeepSeek 做了更稳定的归一化改进
\(L_{\text{ExpBal}} = \alpha_1 \sum_{i=1}^{E} f_i P_i\) 其中: \(f_i = \frac{E}{E_\text{active}} \cdot \frac{\text{tokens to } i}{\text{tokens total}}, \quad P_i = \frac{1}{T} \sum_{t=1}^{T} s_{i,t}\) 子公式 1 — 实际负载比例: \([ f_i = \frac{\text{experts}}{\text{activated experts}} \cdot \frac{\text{tokens to expert } i}{\text{tokens total}} ]\) 说明:
- 如果所有专家都均匀接收 token,( f_i ) 应该接近 1;
- 若某个专家收到太多 token,则 ( f_i > 1 ),触发更高的惩罚。
这个损失项强制 Router 的分配概率 $P_i $ 与实际负载 $ f_i $ 对齐, 防止 Router 倾向于将大部分 token 路由到少数专家。
4.3.2 Device-Level Balance Loss(设备级负载均衡)
由于 DeepSeek V3 的专家被跨 GPU 分组(Expert Grouping), 即不同 GPU 存放不同专家,因此即便专家级平衡了 GPU 之间的计算负载也可能不均(某台 GPU 的专家更“热门”)
为此,DeepSeek 引入第二个平衡项: \(L_{\text{DevBal}} = \alpha_2 \sum_{j=1}^{G} f_j P_j\) 其中: \(f_j = \text{avg}(f_i) \text{ for } i \in j, \quad P_j = \sum_{i \in j} P_i\)
这个损失项在更高层次上约束:
**不同 GPU 上的专家组负载要尽量均衡 **
它能防止:
- 部分 GPU 因热门专家而计算密集、通信繁重;
- 其他 GPU 几乎空闲,资源利用率低。
4.3.3 总损失
通过组合: \(L_{\text{total}} = L_{\text{ExpBal}} + L_{\text{DevBal}}\)
DeepSeek 实现了在 跨节点 MoE 并行训练 中 同时保持专家使用率均衡与 GPU 计算资源高效利用。
5. DeepSpeed MoE 实现
import torch
import deepspeed
import deepspeed.utils.groups as groups
from deepspeed.moe.layer import MoE
WORLD_SIZE = 4
EP_WORLD_SIZE = 2
EXPERTS = 8
fc3 = torch.nn.Linear(84, 84)
fc3 = MoE(hidden_size=84, expert=self.fc3, num_experts=EXPERTS, ep_size=EP_WORLD_SIZE, k=1)
fc4 = torch.nn.Linear(84, 10)
https://github.com/deepspeedai/DeepSpeed/blob/master/deepspeed/moe/layer.py
class MoE(nn.Module):
"""Initialize an MoE layer.
Arguments:
hidden_size (int): the hidden dimension of the model, importantly this is also the input and output dimension.
expert (nn.Module): the torch module that defines the expert (e.g., MLP, torch.linear).
num_experts (int, optional): default=1, the total number of experts per layer.
ep_size (int, optional): default=1, number of ranks in the expert parallel world or group.
k (int, optional): default=1, top-k gating value, only supports k=1 or k=2.
capacity_factor (float, optional): default=1.0, the capacity of the expert at training time.
eval_capacity_factor (float, optional): default=1.0, the capacity of the expert at eval time.
min_capacity (int, optional): default=4, the minimum capacity per expert regardless of the capacity_factor.
use_residual (bool, optional): default=False, make this MoE layer a Residual MoE (https://arxiv.org/abs/2201.05596) layer.
noisy_gate_policy (str, optional): default=None, noisy gate policy, valid options are 'Jitter', 'RSample' or 'None'.
drop_tokens (bool, optional): default=True, whether to drop tokens - (setting to False is equivalent to infinite capacity).
use_rts (bool, optional): default=True, whether to use Random Token Selection.
use_tutel (bool, optional): default=False, whether to use Tutel optimizations (if installed).
enable_expert_tensor_parallelism (bool, optional): default=False, whether to use tensor parallelism for experts
top2_2nd_expert_sampling (bool, optional): default=True, whether to perform sampling for 2nd expert
"""
def __init__(self,
hidden_size: int,
expert: nn.Module,
num_experts: int = 1,
ep_size: int = 1,
k: int = 1,
capacity_factor: float = 1.0,
eval_capacity_factor: float = 1.0,
min_capacity: int = 4,
use_residual: bool = False,
noisy_gate_policy: Optional[str] = None,
drop_tokens: bool = True,
use_rts: bool = True,
use_tutel: bool = False,
enable_expert_tensor_parallelism: bool = False,
top2_2nd_expert_sampling: bool = True) -> None:
super(MoE, self).__init__()
self.use_residual = use_residual
self.enable_expert_tensor_parallelism = enable_expert_tensor_parallelism
assert num_experts % ep_size == 0, f"Number of experts ({num_experts}) should be divisible by expert parallel size ({ep_size})"
self.ep_size = ep_size
self.expert_group_name = f"ep_size_{self.ep_size}"
self.num_experts = num_experts
self.num_local_experts = num_experts // self.ep_size
log_dist(
f'Creating MoE layer with num_experts: {num_experts} | num_local_experts: {self.num_local_experts} | expert_parallel_size: {self.ep_size}',
[0])
assert noisy_gate_policy is None or noisy_gate_policy in ['None', 'Jitter', 'RSample'], \
'Unsupported noisy_gate_policy: ' + noisy_gate_policy
experts = Experts(expert, self.num_local_experts, self.expert_group_name)
self.deepspeed_moe = MOELayer(TopKGate(hidden_size, num_experts, k, capacity_factor, eval_capacity_factor,
min_capacity, noisy_gate_policy, drop_tokens, use_rts, None,
top2_2nd_expert_sampling),
experts,
self.expert_group_name,
self.ep_size,
self.num_local_experts,
use_tutel=use_tutel)
if self.use_residual:
self.mlp = expert
# coefficient is used for weighted sum of the output of expert and mlp
self.coefficient = nn.Linear(hidden_size, 2)
def set_deepspeed_parallelism(self, use_data_before_expert_parallel_: bool = False) -> None:
self._create_process_groups(use_data_before_expert_parallel_=use_data_before_expert_parallel_)
def _create_process_groups(self, use_data_before_expert_parallel_: bool = False) -> None:
# Create process group for a layer if needed
if self.expert_group_name not in groups._get_expert_parallel_group_dict():
print(f"No existing process group found, creating a new group named: {self.expert_group_name}")
if (groups.mpu is None) or (not self.enable_expert_tensor_parallelism):
# Condition 1 - no groups.mpu means no tensor parallelism
# Condition 2 - disabling expert tensor parallelism on purpose
groups._create_expert_and_data_parallel(
self.ep_size, use_data_before_expert_parallel_=use_data_before_expert_parallel_)
else:
# expert tensor parallelism is enabled
groups._create_expert_data_and_model_parallel(
self.ep_size, mpu=groups.mpu, use_data_before_expert_parallel_=use_data_before_expert_parallel_)
# Set the group handle for the MOELayer (deepspeed_moe) object
self.deepspeed_moe._set_ep_group(groups._get_expert_parallel_group(self.expert_group_name))
def forward(self,
hidden_states: torch.Tensor,
used_token: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None) -> Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]:
""" MoE forward
Arguments:
hidden_states (Tensor): input to the layer
used_token (Tensor, optional): default: None, mask only used tokens
Returns:
A tuple including output, gate loss, and expert count.
* output (Tensor): output of the model
* l_aux (Tensor): gate loss value
* exp_counts (Tensor): expert count
"""
output = self.deepspeed_moe(hidden_states, used_token)
if self.use_residual:
# Residual MoE
output_mlp = self.mlp(hidden_states)
if isinstance(output_mlp, tuple):
output_mlp = output_mlp[0] # Ignore the bias term for now
coef = self.coefficient(hidden_states)
coef = F.softmax(coef, dim=-1)
output = output * coef[..., 0:1] + output_mlp * coef[..., 1:]
return output, self.deepspeed_moe.l_aux, self.deepspeed_moe.exp_counts
参考:
- DeepSpeed 官方文档: https://www.deepspeed.ai/tutorials/mixture-of-experts/